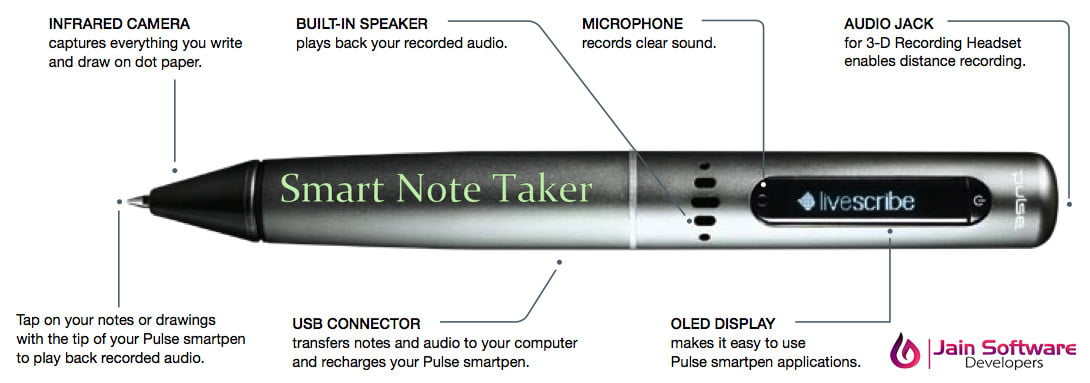
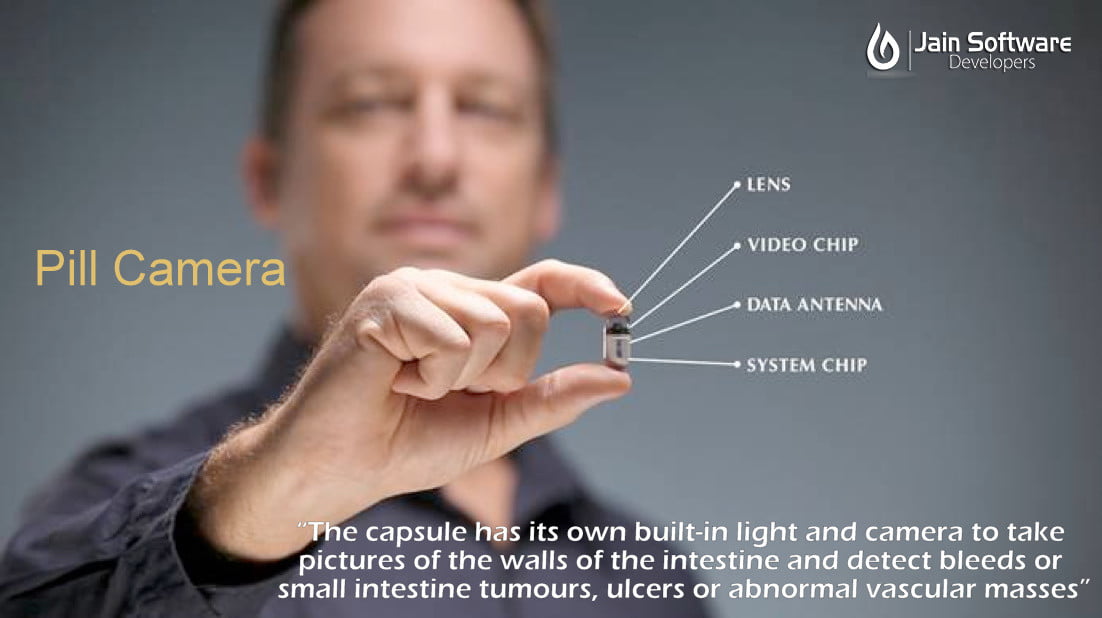
Why Should We Go For A Website?
In Business, Official BlogThe Importance and Purpose of Websites in the Modern World
By Author – Prankul Sinha
In today’s digital era, having a website is one of the easiest and most effective ways for any business to showcase and advertise its products. A well-designed website not only displays products beautifully but also helps a company build a strong relationship with its customers. It serves as a powerful online presence where customers can easily learn more about your offerings and even make purchases directly.
When a business has its own website, it experiences significant growth. A good website design attracts more visitors, which often leads to an increase in sales. Moreover, it allows business owners to track company performance conveniently from their phones or laptops — anytime, anywhere.
Websites are also useful for hiring. If a company is looking to recruit new employees, it can simply post job openings on its website, making it easy for potential candidates to apply online.
Websites in Education
In today’s world, schools and colleges are also relying heavily on websites. They use them not only to promote their institutions but also to manage many daily activities. Students can pay their fees through online portals, check announcements about events, and stay updated on all school or college activities.
Thus, the purpose of a website varies depending on the need — from business promotion to e-commerce, education, and entertainment. Below are a few examples:
1. The Purpose of E-Commerce Websites
The primary goal of e-commerce websites is to sell products online. Successful e-commerce sites are optimized to increase conversions — ensuring visitors make purchases with ease.
To achieve this, such websites use modern design and marketing strategies, smooth navigation, fast checkout systems, and multiple secure payment options. Reducing friction during the shopping process helps build customer trust and boosts sales.
2. The Purpose of Service-Based Business Websites
Service-based business websites aim to convince visitors to become customers. They build credibility by presenting the company as professional, experienced, and reliable.
Before reaching out, customers often review websites to evaluate a company’s expertise, reputation, and service quality. Including client testimonials, visual portfolios, and informative articles helps build trust and demonstrate authority in the field.
A well-structured service-based website ensures potential clients feel confident about choosing that company over others.
3. The Purpose of Social Media Websites
The main purpose of social media websites is to connect people — friends, families, and communities — allowing them to share photos, videos, and experiences.
However, social networks are not limited to personal use. Businesses use social platforms to build direct relationships with their customers, receive valuable feedback, and understand what their audience truly needs and expects.
4. The Purpose of Entertainment Websites
Entertainment websites are designed to engage and amuse visitors. These may include online magazines, celebrity news portals, sports updates, movies, humor, and more.
To keep users returning, these sites are updated frequently and offer interactive content such as videos, podcasts, and slideshows. An engaging entertainment website provides a fun and refreshing online experience for its audience.
Conclusion
In short, websites play an essential role in every field — from business and education to entertainment and social connection. They have become the digital face of modern organizations, helping them grow, communicate, and connect with the world more effectively.
Having a well-designed and functional website is no longer a luxury — it’s a necessity for anyone who wants to succeed in today’s fast-paced digital world.