Smart Note Taker
In Business, Official Blog, Tech-BLOG, TechnicalSmart Note Taker :-
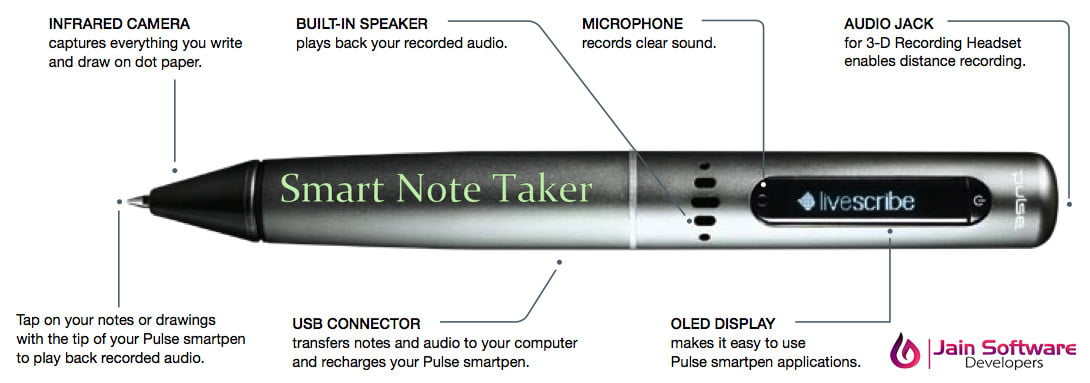
The Smart Note Taker is such a helpful product that satisfies the needs of the people in today’s technological and fast life. This product can be used in many ways. The Smart NoteTaker provides taking fast and easy notes to people who are busy with something else. With the help of Smart NoteTaker, people will be able to write notes on the air, while being busy with their work
The written note will be stored on the memory chip of the pen and will be able to read in digital medium after the job has done. This will save time and ease life. The smart note taker is good and helpful for blinds that think and write freely. Another place, where this product can play an important role, is where two people talks on the phone. The subscribers are apart from each other while their talk and they may want to use figures or texts to understand themselves better. It’s also useful especially for instructions in presentations.
The instructors may not want to present the lecture in front of the board. The drawn figure can be processed and directly sent to the server computer in the room. The server computer then can broadcast the drawn shape through network to all of the computers which are present in the room. By this way, the lectures are aimed to be more efficient and fun. This product will be simple but powerful. The product will be able to sense 3D shapes and motions that user tries to draw. The sensed information will be processed and transferred to the memory chip and then will be monitored on the display device. The drawn shape then can be broadcasted to the network or sent to a mobile device.
“Technology is the best when it brings people together”
Technical Definition of Smart Note Taker:-
In order to meet the technical requirements of the product we need Operating System Like Windows or Linux in order to implement software part of the project, Displacement Sensors to recognize the displacement of the pen in three dimensions, parallel cable to communicate with computer, software to solve the displacement data and finds the individual coordinate displacements in three axes and transform the data into text format, analog to digital converter to process analog displacement data and convert them into digital format, switch to control the pen and Rechargeable battery.
- Analog to digital converter
- Software program to convert data into text or string format
- Operating System ??Parallel cable
- Switch
- Rechargeable battery
- Displacement Sensor
“It’s Not faith in technology, It’s Faith in People“
Note Taker for PC:-
PC Notes Taker is the world’s first device that captures natural handwriting on any surface onto a PC in real time. Based on a revolutionary electronic pen, PC Notes Taker displays the user’s handwritten notes, memos or drawings on the computer, and stores the image for future use. PC Notes Taker is ideal for markets where the handwritten input is essential, such as health, educational and financial sectors. Supplied with user-friendly software, PC Notes Taker is compatible with PCs and notebooks.
Adds Handwriting Input to any Computer PC Notes Taker is the world’s first device that captures natural handwriting on any surface onto a PC in real time. Based on a revolutionary electronic pen, PC Notes Taker displays the user’s handwritten notes, memos or drawings on the computer, and stores the image for future use. PC Notes Taker is ideal for markets where the handwritten input is essential, such as health, educational and financial sectors. Supplied with user-friendly software, PC Notes Taker is compatible with PCs and notebooks.
Features:-
Capture of handwriting from any plain paper or other writing surface Input of continuous writing up to A4 page size Insert sketches, signatures, equations, and notes into Word documents E-mail sketches or handwritten notes in any language using MS OUTLOOK Convert handwriting to digital text using MS word recognition engine Annotate, add comments, edit and draw in your own handwriting onto MS office documents Create instant messaging using ICQ
The Smart Pen system includes the Smart Pen and a pen cradle connected to an internet-enabled computer. As CRFs are filled out, the Smart Pen records each stroke. It identifies each CRF and where it is on the page through a very fine grid pattern that appears as a light gray background shading on the CRF. The Pen is then placed in the cradle, activating a password-protected Internet link to Health Decisions. Data are interpreted into fields and validation can occur immediately, with queries returned to sites quickly over the Internet. The process also creates an exact copy of the original CRF that can be read for notation and comparison with interpreted data fields. Health Decisions takes the best technology and applies it to your clinical trials.
“In Technology Whatever can be done will be done”
Note Taker for mobile:-
The Ultimate Handwriting Capture Device Mobile NoteTakerTM is the worlds first portable handwriting capture device based on natural handwriting as an input. Attach plain paper of any kind and use the Pegasus electronic pen to capture, store and share handwritten drawings, sketches, notes, and memos at meetings, lectures, and conferences.
Mobile NoteTakerTM has a built-in LCD to confirm input. The on-board flash memory can store up to 50 pages.
Features:-
Uses standard paper – no special paper required Stores up to 50 A4 pages Includes LCD to view and confirm input Operates both in mobile mode and when connected to PC, notebook or other device Connects to PC/Notebook via USB cable (included) Includes software for synchronization and management of stored files Writes directly into MS Office applications (in Connected mode) Allows file transfer over LAN, email, and instant messaging application (in connected mode).
Capture, Organize, and Share Your Notes Digitally-Anywhere, Anytime!
Mobile Mode Enables capture and storage of notes and sketches digitally at meetings, lectures, and conferences.
“Because People who are crazy enough to think they can change the world are the ones who do”
Connected Mode
Synchronizes the Mobile NoteTakerTM and a PC/Notebook via USB cable (included). You can upload, organize, move, edit or add to handwritten notes, ideas, sketches, phone numbers, or reminders. The included software also enables memos, notes, and sketches to be sent via e-mail or over the LAN network. It is also possible to write directly into MS Word or Outlook, and add a personal touch to ICQ instant messages. Based on Pegasus successful PC Notes Taker, Mobile NoteTakerTM is the ultimate handwriting capture device. Everything you need to get started is right in the box. Even if you dont have standard size paper or piece of paper with you-you can use anything – an envelope, an old receipt, a tear-off from a paper bag and best of all in your own natural and writing.
As long as you have the Mobile NoteTakerTM, you can jot down your most inspired ideas and be sure that you will never lose them again.